Identifying and Describing Information Seeking Tasks
Authors: C. Satterfield, T. Fritz, G. C. Murphy.
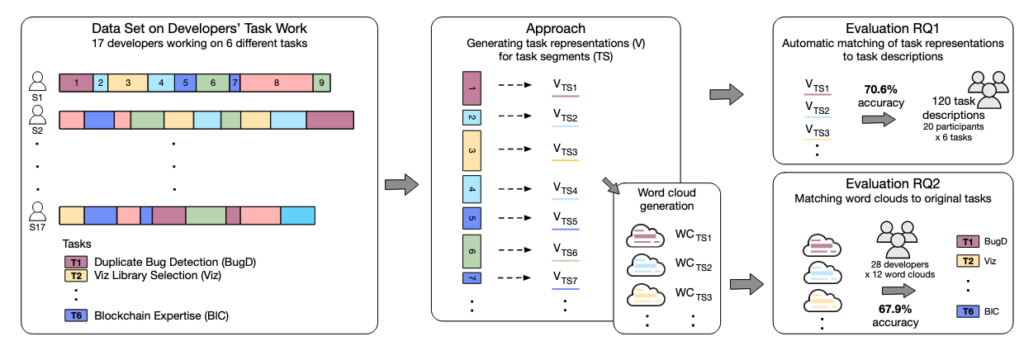
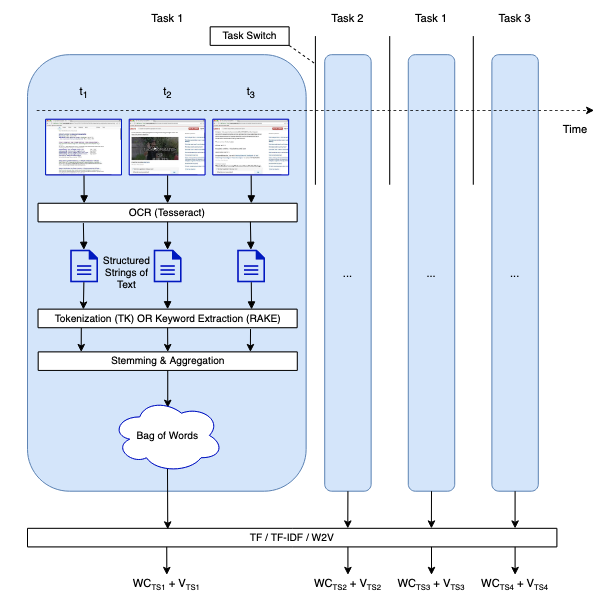
A software developer works on many tasks per day, frequently switching between these tasks back and forth. This constant churn of tasks makes it difficult for a developer to know the specifics of when they worked on what task, complicating task resumption, planning, retrospection, and reporting activities. In a first step towards an automated aid to this issue, we introduce a new approach to help identify the topic of work during an information seeking task — one of the most common types of tasks that software developers face — that is based on capturing the contents of the developer’s active window at regular intervals and creating a vector representation of key information the developer viewed. To evaluate our approach, we created a data set with multiple developers working on the same set of six information seeking tasks that we also make available for other researchers to investigate similar approaches. Our analysis shows that our approach enables: 1) segments of a developer’s work to be automatically associated with a task from a known set of tasks with average accuracy of 70.6%, and 2) a word cloud describing a segment of work that a developer can use to recognize a task with average accuracy of 67.9%.